IBC Eureka Technical Walkthrough

This article was written by Susannah Evans, Product Manager at Cosmos Labs. Follow Susannah on X at @susevans or on Github. The IBC team at Cosmos Labs contributed to this article.
Interoperability between blockchains is vital for user onboarding. This blog post covers how IBC Eureka works, the new onboarding solution for Cosmos chains that provides a fast and cheap solution to connect to Ethereum with more rollups and domains to be added in the future.
TL;DR:
- IBC Eureka simplifies cross-chain communication between Cosmos and Ethereum by reducing infrastructure overhead, improving usability, and enabling seamless token transfers and onboarding.
- Built on IBC v2, Skip:Go, and the Cosmos Hub, Eureka leverages secure light clients, efficient relaying, and smart contracts to deliver fast and affordable bridging, with support for one-click routes between Cosmos and Ethereum.
- The Cosmos Hub acts as a powerful entry point into the Cosmos ecosystem. It offers benefits like reduced maintenance, lower costs via batching, and compatibility with existing IBC infrastructure, though it is not mandatory for integration.
Why IBC Eureka?
Cosmos stands for sovereignty and flexibility. If you can imagine the application, you can build it: it is not a case of if, but how. These values lead to projects carving out a niche, especially application-specific blockchains. These chains come with ‘out of the box’ interoperability that only requires trust between the chains that want to communicate: tokens, data, and information can move freely. However, IBC Classic has limited extensibility and has a large infrastructure overhead. The pace of expansion of the IBC network could not meet the demands of its users, and third-party bridge integrations were required to reach these domains.
IBC Eureka provides Cosmos blockchains with an onboarding and interoperability solution that removes the limitations of the pre-Eureka era. It reduces infrastructure overhead and the complex usability of knowing which channel takes you to which chain or dropped packets. Instead, chains can focus on their own niche and realise their ambitions as application-specific blockchains. The first connection is to Ethereum; more chains and L2s will be added in the near future.
How IBC Eureka Works: A Technical Explanation of the Product
IBC Eureka is composed of 3 elements: IBC v2, Skip Go, and the Cosmos Hub. This combination plays to the strength of each component to offer a secure, fast and affordable onboarding experience between Cosmos and Ethereum.
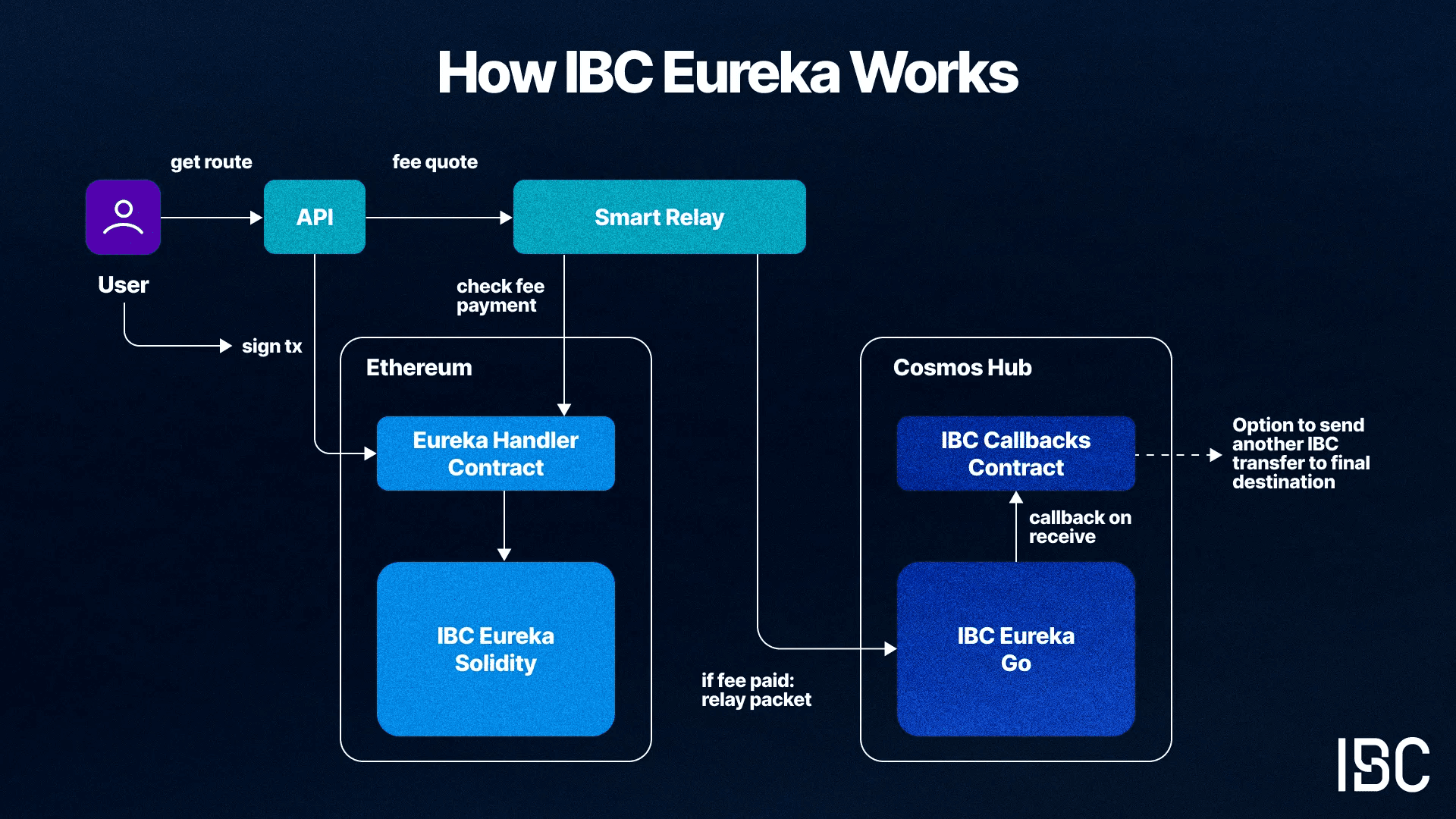
Overview of transaction lifecycle with IBC Eureka
IBC v2
IBC v2 is the iteration of the IBC protocol that removes the shortcomings of IBC Classic. It builds upon light client security, extensibility, and application composability whilst removing complexity. The Go and Solidity deployments provide the means to bridge tokens between Cosmos and Ethereum through the implementation of token transfer (ICS20) in each domain.
The connection is underpinned by light clients, the gold standard in cross-chain communication, which enables communication through trusting the underlying blockchains. An Ethereum light client as a CosmWasm contract is deployed on the Cosmos Hub using the 08-wasm client, and Succinct’s SP1 zkVM is used to run a tendermint-rs light client of the Cosmos Hub with proofs posted to Ethereum, which enables cost-effective light client verification.
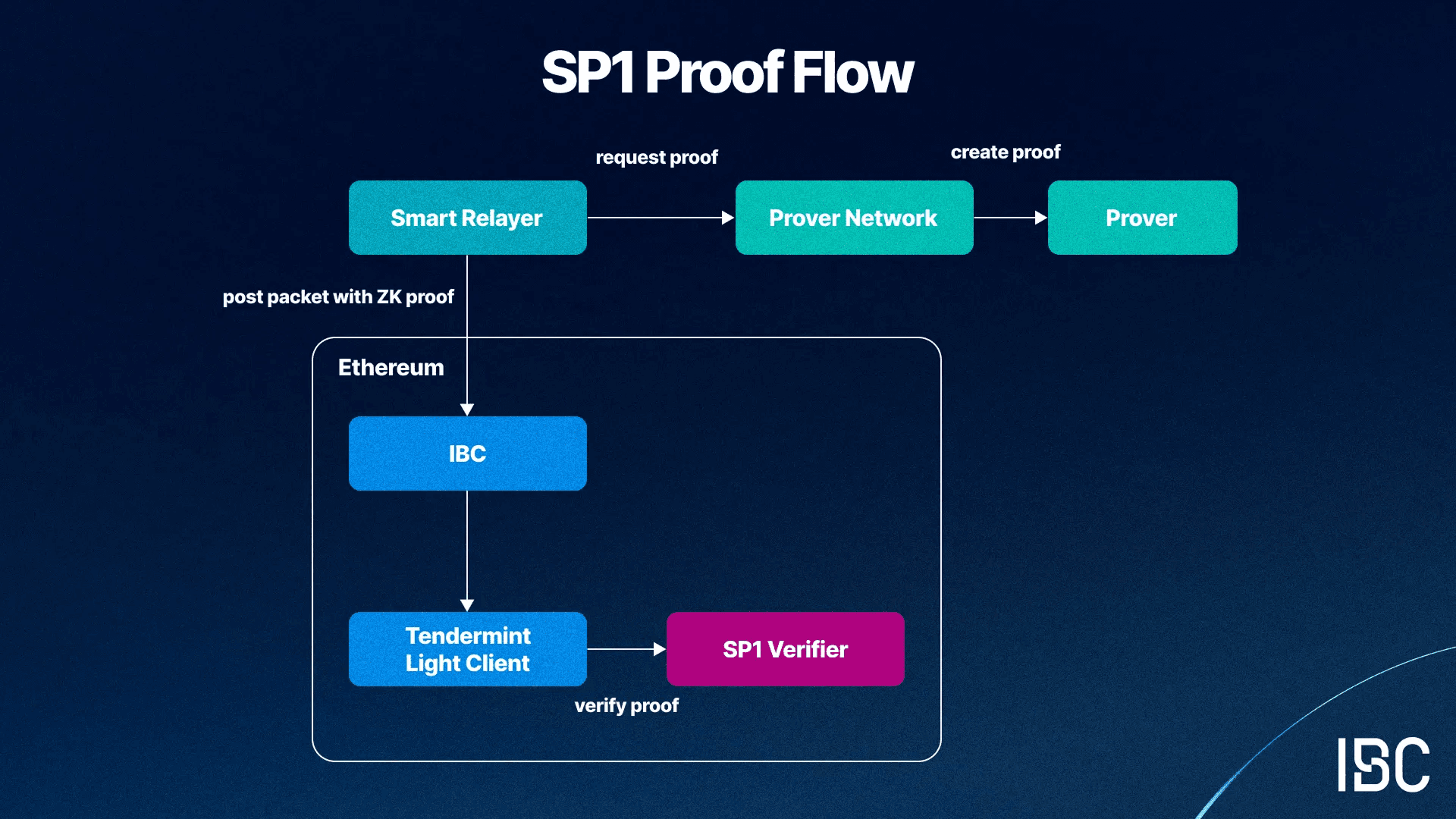
The lifecycle of a proof with SP1 for verifying the consensus of a Cosmos Chain on Ethereum.
To learn more about IBC v2, check out this introductory blog post, or for a deeper understanding, read the protocol specification.
Skip:Go
Skip:Go combines an API, on-chain smart contracts, smart relay, and Go Fast, the solver network, to handle transaction generation and execution for users. It is the interface that users will interact with to use IBC Eureka.
The smart relay, which has been used for CTTP relaying, has been adapted to work with IBC v2. As gas is significantly more expensive on Ethereum than Cosmos chains, it would be untenable to use the existing relayer approach, where off-chain agreements are made with specific operators. Instead, end users pay a relay fee to cover the gas costs on the destination chain.
The Skip:Go contracts handle relay fees. On Ethereum, there is a specific IBC Eureka handler contract that wraps the IBC v2 contracts and calls into token transfer once relay payment has been made. On the Cosmos Hub, the callbacks middleware is used to create a new IBC packet on receiving a packet from Ethereum, to send on to the final destination using the existing IBC Classic network. The reverse direction mirrors the flow. Fee payments are taken in the token being transferred. For example, if ATOM is being sent from the Hub to Ethereum, ATOM is deposited into the Cosmos Hub Eureka contract to cover the gas fees on Ethereum paid by the smart relayer.
The API provides endpoints to generate the transaction format needed to use Eureka and the ability to track the status of the transaction through its lifecycle. For example, a user may want to bridge SolvBTC from Ethereum to Babylon, which would require an IBC v2 transaction combined with an IBC classic transaction. Using the Skip:Go contracts, this route is possible with a single signature for the user.
Ethereum finality takes between 15–20 minutes. For users that do not want to wait this long, they can benefit from the Go Fast solver network. As long as there is liquidity for the asset to swap into within the Cosmos ecosystem in an integrated DEX, users can receive their assets in 30 seconds or less.
Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub was the first chain in Cosmos, and today, it has over 74 connected chains, hundreds of centralised exchange integrations, and it is validated by the top infrastructure providers. It provides an entry point to access Ethereum initially, with many more networks added in the future.
There are many benefits to routing through the Hub, these include:
- An integrator needs to maintain a single IBC connection to the Cosmos Hub for all of their onboarding needs to be met.
- There is no overhead of maintaining multiple relayers.
- It avoids having to deal with client expiry for less active connections as all traffic is aggregated.
- There is a cost-benefit to end users, as packet batching reduces the cost of going into Ethereum.
- Chains do not have to perform a chain upgrade to access IBC Eureka, as IBC Classic is backward compatible with every version of ibc-go.
Note that there is no requirement to route through the Cosmos Hub, but as more bridges are onboarded, particularly with chains that do not have light client support, it is only possible to access attestation services through the Hub. This means future access to rollups, such as Base or Arbitrum.
How to benefit from IBC Eureka and Integrate It
If you are interested in using IBC Eureka, take a look at our documentation and get in touch with us via this interest form. Try out asset transfers between Ethereum and Cosmos chains, such as Babylon or SEDA at go.cosmos.network.
About Cosmos Labs:
Cosmos Labs is the development and growth team for Cosmos, a decentralized network of independent, scalable, sustainable, and interoperable blockchains. Cosmos is one of the largest blockchain ecosystems, with over 250 apps and services and over $41 billion USD market cap.